Egyptian Hieroglyphics
People often refer to Hieroglyphics as the ancient Egyptian
language in fact Hieroglyphics is only a form of writing the Egyptian language.
Hieroglyphs are the pictures used to write the Egyptian language which consisted
of more than 750 individual signs.
There were three forms to write the Egyptian language :
- Hieroglyphics: The form found on monuments, and some papyri. It is made up
of pictures which make up words. The ancient Egyptians called their script
mdju netjer, or "words of the gods." Hieroglyphs were the earliest
form of Egyptian script. Hieroglyphics changed over time. It began with one
symbol for each word then symbols were combined to form words.
- Hieratic: This is script hieroglyphics. It's form varied over the
centuries. Pictures were reduced to lines and squiggles to make writing
quicker.
- Demotic: This was a later script version of Egyptian language which was
not based on hieroglyphics, but was phonetic. Demotic means "the
people's writing." It got this name because many people could read it
The first hieroglyphs appear on labels and pottery objects dated to about
3100 BCE in the late Predynastic Period, and the last glyphs appear on the
island of Philae in a temple inscription carved in 394 ACE. Originally,
hieroglyphs were used to write different kinds of texts on different surfaces,
but as hieratic developed, hieroglyphic script became confined to religious and
monumental useage, mostly carved in stone. The Greeks called the script hiera
grammata, "the sacred letters," or ta hieroglyphica "the sacred
carved letters."
Hieroglyphic script is largely pictorial in character. Most are recognizable
pictures of natural or man-made objects, often symbolically color-painted. The
ground plan of a simple house, or pr, might stand for the word for
"house."
Hieroglyphic script also includes phonograms, sign-words for concepts that
cannot be conveyed by a simple picture. The phonogram is best represented by the
"rebus principle." A rebus is a message spelled out in pictures that
represent sounds rather than the things they are pictures of: for example, the
picture of an eye, a bee and a leaf in English might be used to make the English
sentence "I Believe," or "eye-bee-leaf." The sentence itself
has nothing to do with eyes, bees or leaves.
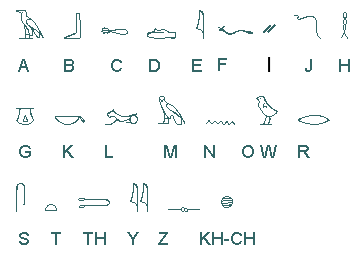
Hieroglyphic Alphabet
|
Get a Silver
Cartouche with Your Name in Hiroglyphics
This is the Hieroglyphic alphabet reduced to approximately match the
English alphabet. words in Egyptian were made up of sounds, partly of
consonants and partly of vowels. But, the writing of hieroglyphs constantly
ignored and omitted vowels. So when you write for example the name Ben in
Hieroglyphics you only use the two letters BN
Egyptian signs were of two types, phonetic signs and determinatives, signs
which gave a clue to the meaning of the word. Most words were made up of
phonetic signs, followed by one determinative. A few had two or three
determinatives. Some very common words had no determinative and some other
common words were written as just the determinative, with no phonetic signs.
There are also common abbreviations, in which one or two signs stand for an
entire word or phrase.
A hieroglyphic inscription is arranged on its surface either in columns or in
horizontal lines. There are no punctuation marks or spaces to indicate the
divisions between words. The signs are generally inscribed facing rightward,
(though the opposite orientation does appear in certain contexts) and are
usually read from right to left; if they appear in horizontal lines, one reads
from upper to lower.
Types of Hieroglyphic Signs
- Alphabetic signs: There are several different kinds of signs in Egyptian.
First we have alphabetic signs. See Egyptian Hieroglyphic Alphabet. Some of
the most common words use only alphabetic signs.
- Determinatives: Most words end in determinative signs. These are
signs which have no sound, but give a clue about the meaning of the word.
- Other phonetic signs: Many words begin with a phonetic sign which is not
alphabetic, but is phonetic. These signs may also appear later in a word.
Most of them represent two or three alphabetic signs, and are called
biliterals and triliterals. They are usually followed by redundant
alphabetic signs which help you tell what the sound of the sign is.
- Abbreviations: Abbreviations are very common. One or two signs often stand
for an entire word.
- Ideograms: A special kind of abbreviation is an ideogram. This is a sign
(occasionally accompanied by a phonetic sign) followed by a vertical line
(or a feminine -t sign, then a vertical line if the word is feminine). This
shows that the sign stands for the actual object that it looks like, more or
less. A circle (sun) with a vertical line under it represents the sun.
The study of Hieroglyphics
Hieroglyphics can be transliterated and translated today, as can hieratic.
Demotic is usually transliterated directly into the letters of the English
alphabet. Many texts can now be read to glimpse how the Egyptians spoke of
themselves, their gods, and their history.
|